SAE 1045 Steel Chemical Composition

The chemical composition of SAE 1045 steel plays a crucial role in determining its mechanical properties. The table below provides an overview of the key elements that make up this carbon steel grade.
Table of contents
- SAE 1045 Steel Chemical Composition
- ASTM 1045 Weldability
- Mechanical Property of AISI 1045 Steel Cold Drawn
- Heat Treatment of DIN 1.1191
- 1045 Steel vs 4140 Steel
- 1045 Quenched and Tempered Steel properties
- AISI 1045 Equivalent Grades
- Thermal Properties of SAE 1045
- Tolerance of AISI 1045 Carbon Steel
- Ck45 Steel Annealing
- Quality Certification of Steel 1045
- AISI 1045 Corrosion Resistance
- Electrical Properties of JIS S45C Steel
- Applications of SAE 1045 Steel
SAE 1045 Steel Chemical Composition
| Grade | C | Si | Mn | P | S |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1045 | 0.43-0.50 | 0.15-0.35 | 0.60-0.90 | ≤0.04 | ≤0.05 |
AISI 1045 Offers Good Weldability, Machinability and High Strength
AISI 1045 is known for its excellent weldability, which makes it ideal for creating strong and durable joints. This feature ensures that the material can withstand structural loads without cracking or failing, making it suitable for critical applications where strength is essential.
In terms of machinability, 1045 steel allows for efficient cutting with minimal tool wear, resulting in better surface finish and tighter tolerances. This not only speeds up production but also reduces manufacturing costs significantly.
Its high tensile strength and impact resistance make it a popular choice for construction and industrial components that must endure heavy loads and harsh environments.
ASTM 1045 Weldability

| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Welding Conditions | AISI 1045 is readily welded with the correct procedure |
| Electrodes | Use low hydrogen electrodes. |
| Pre-heating | Pre-heat workpiece to 200°C – 300°C (392°F – 572°F). |
| Welding Temperature | Maintain pre-heat temperature during welding. |
| Cooling | Cool slowly using sand or ashes to control the cooling rate. |
| Stress Relief | Perform stress relief at 550°C – 660°C (1022°F – 1220°F). |
Mechanical Property of AISI 1045 Steel Cold Drawn
| Mechanical Properties | Hardness, (Brinell hardness) | Hardness, Brinell | Hardness, Rockwell B (Brinell hardness) | Hardness, Vickers ( Brinell hardness) | Tensile Strength, Yield | Tensile Strength, Ultimate | Elongation at Break (in 50 mm) | Reduction of Area | Poissons Ratio (Typical For Steel) | Modulus of Elasticity (Typical for steel) | Bulk Modulus (Typical for steel) | Shear Modulus (Typical for steel) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Metric | 184 | 163 | 84 | 170 | 310 MPa | 565 MPa | 16.00% | 40.00% | 0.29 | 200 GPa | 140 GPa | 80 GPa |
| Imperial | 184 | 163 | 84 | 170 | 45000 psi | 81900 psi | 16.00% | 40.00% | 0.29 | 29000 ksi | 20300 ksi | 11600 ksi |
DIN 1.1191 Material Are Generally Available in Black Hot Rolled or Normalized Conditions
Normalized conditions improve the mechanical properties of the material by reducing internal stresses, refining the grain structure, and enhancing machinability. This makes the steel more uniform and easier to work with during manufacturing processes.
Heat Treatment of DIN 1.1191
| Process | Heating Temperature | Cooling Method |
|---|---|---|
| Forging | 850°C – 1250°C (1562°F – 2282°F) | Cool in a furnace |
| Annealing | 800°C – 850°C (1472°F – 1562°F) | Cool in a furnace |
| Normalizing | 870°C – 920°C (1598°F – 1688°F) | Cool in still air |
| Stress-Relieving | 550°C – 660°C (1022°F – 1220°F) | Cool in still air |
| Hardening | 820°C – 850°C (1508°F – 1562°F) | Quench in water or brine |
| Tempering | 400°C – 650°C (752°F – 1202°F) | Cool in still air |
1045 Steel vs 4140 Steel

| Property | 1045 Steel | 4140 Steel |
|---|---|---|
| Type | Carbon steel | Alloy steel |
| Carbon Content | 0.43-0.50% | 0.40% |
| Manganese Content | 0.60-0.90% | 0.75-1.00% |
| Chromium | None | Present |
| Molybdenum | None | Present |
| Iron (Fe) | 98.51-98.98% | 96.79-97.78% |
| Phosphorus (P, max) | 0.04% | 0.035% |
| Sulfur (S, max) | 0.05% | 0.040% |
| Strength | Good strength and impact resistance | Superior hardness and toughness |
| Common Uses | Machinery parts, automotive components | Axles, gears, shafts |
| Characteristics | Moderate hardness and strength | Enhanced wear resistance and toughness |
1045 Quenched and Tempered Steel properties
| Section size mm | up to 16mm | 17-44 mm | 41-100 mm |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tensile strength Mpa | 700-850 | |650-800 | 630-780 |
| Yield strength Mpa | 500 | 430 | 370 |
| Impact Charpy | 30 | 30 | 30 |
| Elongationin 50mm % | 14 | 16 | 7 |
| Hardness HB | 210-245 | 195-235 | |185-230 |
View the Equivalent Grades of Steel 1045
Understanding equivalent grades is essential when working with different international standards. Below are the equivalent grades for AISI 1045 steel across various countries.
AISI 1045 Equivalent Grades
| Country | USA | British | Japan | Australia |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Standard | ASTM A29 | EN 10083-2 | JIS G051 | AS 1442 |
| Grades | 1045 | C45/1.1191 | S45C | 1045 |
Thermal Properties of SAE 1045
| Properties | Metric | Imperial |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal conductivity | 51.9 W/mK | 360 BTU in/hr.ft2.°F |
| Thermal expansion co-efficient (@0.000-100°C/32-212°F) | 11.2 µm/m°C | 6.22 µm/m°C |
Tolerance of AISI 1045 Carbon Steel
| Surface Finish | Black-Forged | Turned | Black-Rolled | Peeled | Grinding | Polished | Cold Drawn |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tolerance | (0,+5mm) | (0,+3mm) | (0,+1mm) | Best H11 | Best h9 | Best h11 | Best H11 |
Annealing Temperature for Jis S45C Grade is From 790-870 °c
Annealing at this temperature helps to soften the material, improving its machinability and malleability. After annealing, the material should be cooled gradually in a furnace to achieve the desired mechanical properties for specific applications.
Ck45 Steel Annealing
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Purpose of Annealing | Softens surface hardness for improved machinability |
| Annealing Temperature | 820°C to 840°C |
| Holding Time | Sufficient time at annealing temperature |
| Measured Surface Hardness | Typically below 200 HBW (Brinell Hardness) |
Quality Certification of Steel 1045
- Chemical analysis
- Ultrasonic test report
- Non Metallic Inclusion
- Heat Treatment Process
- Mechanical properties
- Surface hardness
- Grain size
- Forging ratio
1045 Carbon Steel is Not Very Resistant to Corrosion in Harsh Environments
Due to its low chromium content, 1045 steel is susceptible to corrosion when exposed to moisture, acidic environments, or saltwater. To prevent degradation, it often requires protective coatings or treatments like galvanization or painting.
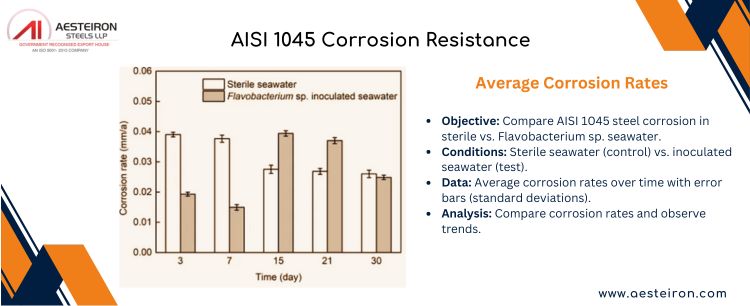
AISI 1045 Corrosion Resistance
| Feature | 1045 Steel |
|---|---|
| Primary Composition | 0.45% Carbon, Iron |
| Corrosion Resistance | Low |
| Protective Layer | Does not form a protective chromium oxide layer |
| Exposure to Harsh Environments | Prone to rust and corrosion in salt water, acids, and bases |
| Maintenance Requirements | Requires coating or treatment for better resistance |
| Typical Applications | Structural components, machinery, automotive parts |
Electrical Properties of JIS S45C Steel
| Electrical Properties | Metric | English | Comments |
|---|---|---|---|
| Electrical Resistivity | 0.0000162 ohm-cm Temperature 0.000 °C |
0.0000162 ohm-cm Temperature 32.0 °F |
annealed specimen |
| 0.0000223 ohm-cm Temperature 100 °C |
0.0000223 ohm-cm Temperature 212 °F |
annealed specimen |
Applications of SAE 1045 Steel
| Pins | Gears | Rams |
| Ratchets | Bolts | Light gears |
| Rolls | Shafts | Sockets |
| Spindles | Axles | Worms |
| Crankshafts | Studs | Guide rods |
| Torsion bars | Connecting rods | Hydraulic clamps |
Welding wires are consumable electrodes used in the process of welding. They are made of various materials, such as carbon steel, stainless steel, aluminum, and flux-cored wire. Welding wires are designed to melt and join two or more metal pieces together when an electric current passes through them. They come in different diameters and compositions to suit different welding applications. Welding wires can be used with different types of welding processes, including MIG (Metal Inert Gas) welding, TIG (Tungsten Inert Gas) welding, and flux-cored arc welding
Welding Wires,Welding Wire Price,Stainless Welding Wire,Stainless Steel Welding Wire
Luoyang Golden Egret Geotools Co., Ltd. , https://www.xtc-thermalspray.com